Robots have long been associated with rigid structures and mechanical movements. However, a groundbreaking invention is reshaping that perception. Researchers at Harvard University have developed the world’s first completely soft, autonomous robot, known as the octobot.
Unlike traditional robots, this revolutionary creation moves without wires, batteries, or hard materials, making it more flexible and adaptable. Inspired by the octopus, which has no internal skeleton, the octobot marks a significant advancement in robotics and automation.
A New Era in Robotics
The development of soft robotics has accelerated in recent years, but most designs still contained rigid components. Before the octobot, engineers relied on hybrid models that combined soft exteriors with hard internal mechanisms or tethered designs that required external power sources. These limitations restricted their versatility and interaction with humans.
Now, the octobot eliminates these constraints by functioning independently. It uses a pneumatic system powered by chemical reactions. The robot’s internal circuit converts liquid hydrogen peroxide into gas, which inflates its limbs, allowing them to move. This system enables the octobot to operate without relying on external controls.
Innovative 3D-Printed Design
Image by Harvard Magazine | Harvard engineers create a flexible octobot.
Harvard’s engineering team, led by Robert Wood and Jennifer Lewis, experimented with over 300 designs before finalizing a successful prototype. They utilized 3D printing technology to construct the robot entirely from silicone materials, ensuring durability and flexibility.
The printing process allowed them to integrate multiple components seamlessly, avoiding the need for assembly of separate mechanical parts. As a result, the octobot exhibits fluid movements, making it safer for human interaction.
The Advantages of Soft Robotics
Soft robots offer several advantages over traditional machines, particularly in safety and adaptability. Unlike rigid robots that pose risks in human-centered environments, soft robots provide a gentler alternative.
1. Enhanced Safety – If a soft robot collides with a person, the impact resembles bumping into a balloon rather than a hard metal structure.
2. Greater Flexibility – Their bendable form allows them to navigate tight spaces and handle delicate objects with ease.
3. Improved Biocompatibility – Scientists can create soft robots using biodegradable materials, reducing their environmental impact.
According to Wood, traditional robots are excellent for automated tasks, but they lack the adaptability required for human interactions. The octobot, however, presents a safer and more interactive alternative.
Potential Applications of Soft Robots
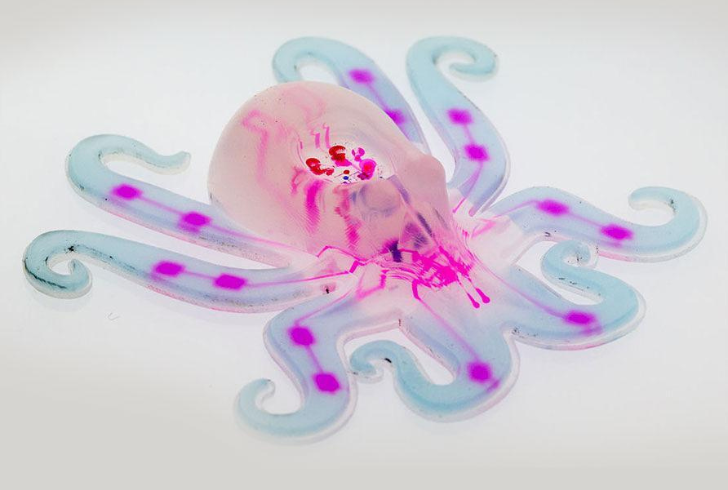

Instagram | luxchin | Soft robots could transform healthcare search missions and ocean exploration.
The introduction of soft robotics opens new doors for medical, industrial, and exploratory applications. Researchers believe the octobot’s technology could transform various fields, including:
1. Healthcare – Soft robots could assist in non-invasive medical procedures, such as swallowable capsules for endoscopies.
2. Search and Rescue Missions – Their flexible nature allows them to navigate debris and reach trapped individuals in emergency situations.
3. Marine Exploration – Inspired by the octopus, these robots could explore underwater environments without disturbing fragile ecosystems.
The Future of Soft Robotics
While the octobot remains a prototype, its success paves the way for more advanced soft robots. Scientists continue to refine the design, aiming to enhance mobility, efficiency, and durability. With ongoing research, future models could feature greater autonomy and expanded capabilities.
As technology evolves, soft robotics will likely become an integral part of various industries. With innovations like the octobot, the future of robotics looks softer, safer, and more adaptable than ever before.











